Click here to see all images
December, 2020
Case of the Month
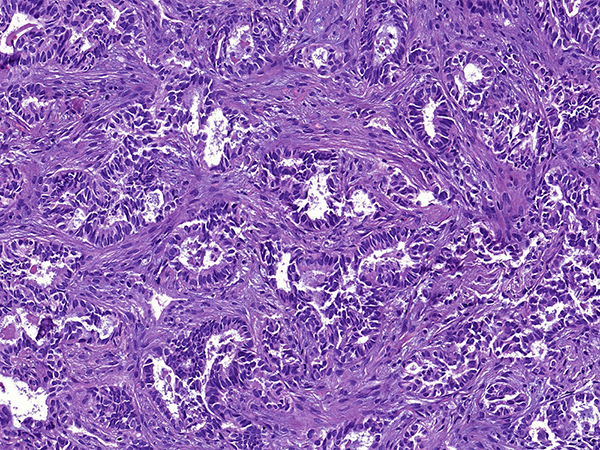
Clinical History: A 70-year-old woman consulted our hospital for a second opinion. She had a history of endometrial carcinoma treated with hysterectomy 5 years prior and was free of disease at last follow-up. She was a sporadic smoker. A chest CT revealed a 3.3-cm solitary lung mass in the left upper lobe without mediastinal lymphadenopathy. CT-guided core needle biopsy was performed (Figures 1-3). Results of immunohistochemical stains are shown in Figure 4 (PAX-8), Figure 5 (TTF-1; 8G7G3/1) and Figure 6 (GATA-3). The neoplastic cells were negative for napsin A, thyroglobulin and estrogen receptors (ER).
Quiz:
Q1. Is it necessary to perform immunohistochemical staining in this case?
- Yes. Given the history and morphology, both primary lung adenocarcinoma and a metastasis from the endometrium need to be considered.
- Yes. Immunostaining for TTF-1 is necessary because a negative TTF-1 stain will exclude a lung primary.
- No. The prior endometrial tumor was diagnosed too long ago, and the clinical setting fits with lung cancer. Save tissue for molecular testing and PD-L1.
- No. There are no helpful immunohistochemical markers in this context because TTF-1 can be positive in gynecologic cancer and PAX-8 is commonly positive in lung adenocarcinomas.
Q2. Which of these statements is true?
- The absence of necrosis excludes a metastasis.
- 8G7G3/1 is the most specific clone of TTF-1.
- A uniform pattern through the biopsy is suggestive of a lung primary.
- All TTF-1 clones are identical in terms of sensitivity and specificity.
Q3. Which of the following is the most helpful immunohistochemical finding in this case?
- Positivity for GATA-3. This suggests a breast primary. A comment should be added suggesting mammography.
- Positive staining for TTF-1. This result narrows the differential to lung and thyroid.
- Strong and diffuse positivity for PAX-8. This argues strongly against lung adenocarcinoma.
- Negative staining for napsin A. This excludes a lung primary.
Answers to Quiz
Q2. B
Q3. C
Diagnosis
Discussion
TTF-1 is a widely used immunohistochemical marker of lung origin. The clone 8G7G3/1 is more specific than SPT24 and SP141. However, even the 8G7G3/1 clone of TTF-1 can be positive in adenocarcinomas from primary sites other than the lung. In the differential between primary lung adenocarcinoma and metastasis to the lung from sites such as the endometrium, kidney and thyroid, it is important to remember that PAX-8 is negative in the vast majority of primary lung adenocarcinomas. In a recent study of 418 resected primary lung carcinomas, not even a single case showed strong and diffuse PAX-8 staining.
Take home message for trainees: Strong and diffuse PAX-8 staining in an adenocarcinoma strongly suggests a non-pulmonary primary.
References
Ordóñez NG. Value of thyroid transcription factor-1 immunostaining in tumor diagnosis: a review and update. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2012;20:429-44.
Pors J, Cheng A, Leo JM, et al. A comparison of GATA3, TTF1, CD10, and calretinin in identifying mesonephric and mesonephric-like carcinomas of the gynecologic tract. Am J Surg Pathol 2018; 42:1596-606.
Contributors
Staff Pathologist
Department of Pathology
HU Vall d’Hebron, Barcelona, Spain
Angel García, MD
Staff Pathologist
Department of Pathology
HU Vall d’Hebron, Barcelona, Spain